Why Is It So Easy to Regain Weight After Dieting?
When people begin their weight loss journey, the first thing that comes to mind is “eating less.” While this approach may show initial results, Cai said the risk of regaining lost weight is extremely high. There are three primary reasons for this pattern:
Decreased Basal Metabolic Rate
When the body senses insufficient caloric intake, it activates a self-protective mechanism, lowering its basal metabolic rate to conserve energy. This metabolic slowdown reduces calorie burning, causing fatigue and a lack of energy. This self-protection also increases cravings for high-calorie foods, making it easy to overeat and regain weight.
Muscle Loss
Dieting not only reduces fat but could also lead to a loss of muscle mass. Because it requires a fair amount of energy to maintain muscles, the body will try to reduce energy consumption by breaking down muscle tissue to make up for the caloric deficit. As muscle loss occurs, metabolism slows further, increasing the risk of weight regain.
Psychological Factors
Humans are not machines. Prolonged, deliberate suppression of the desire to eat can lead to a strong rebound in appetite.
Proper Dietary Proportions Instead of Restriction
Cai warned that some women, particularly those pursuing rapid weight loss, often fail to fully consider the underlying principles of healthy weight management. They may resort to extreme routines, potentially leading to health problems such as anorexia, endocrine disorders, and hair loss. He emphasized that true weight loss does not depend on weight loss products or so-called quick fixes. The key is to establish a healthy, sustainable lifestyle that begins with smart dietary adjustments.
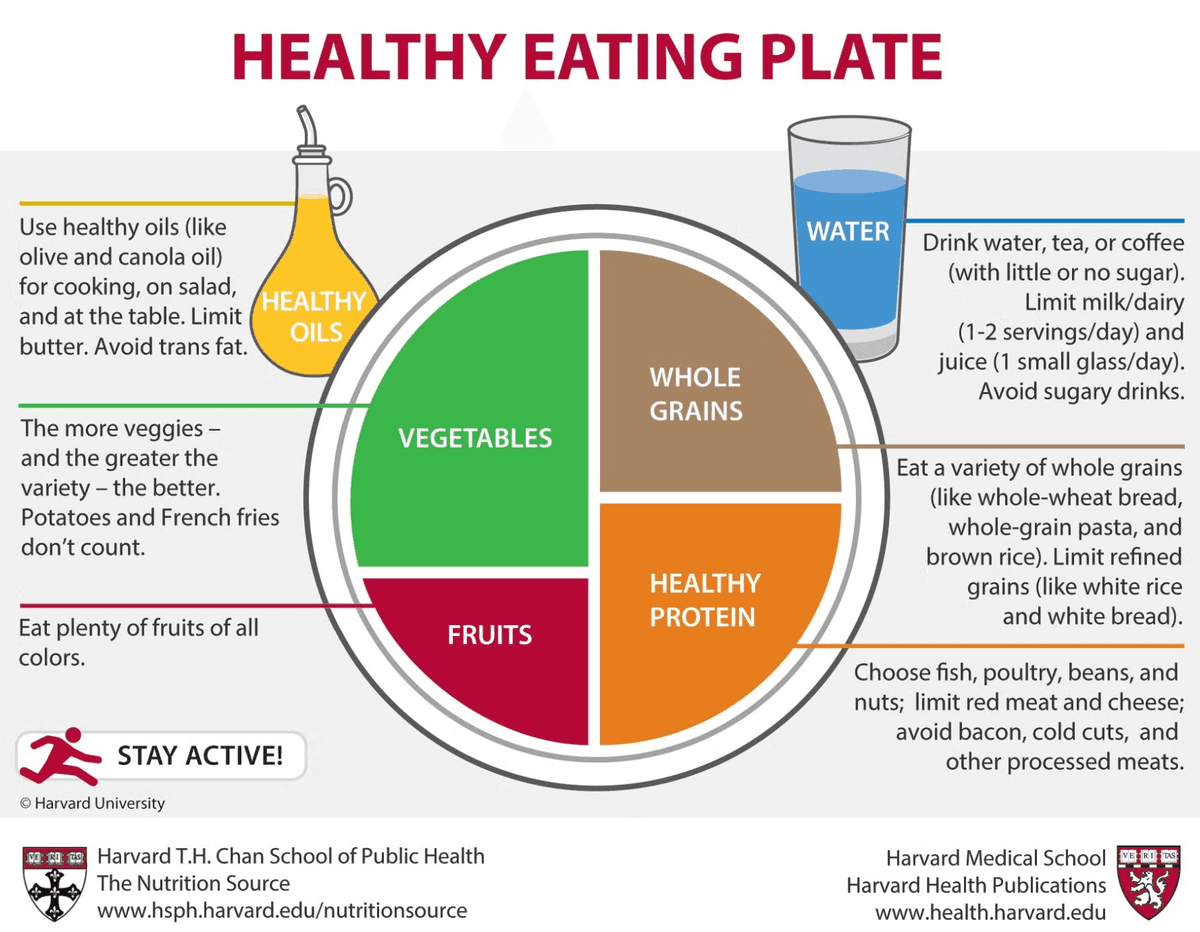
The Harvard Healthy Eating Plate Method
Proper dietary proportions are crucial for maintaining weight and preventing regain. A balanced diet that contains a variety of nutrients helps increase satiety, provides a steady supply of energy, helps control appetite, preserves muscle mass, and maintains a healthy metabolism—all essential for preventing weight regain.
- Upper left section (large section): Include a variety of vegetables, such as leafy greens, carrots, kelp, and mushrooms.
- Lower left section (small section): Include one serving of fruit, about the size of a fist. Fruit provides dietary fiber and contains antioxidants, which may help reduce the risk of obesity.
- Upper right section (starches): Include whole grains, white rice, or noodles. Avoid processed starches high in sugar and oil, such as fried rice and oil-fried noodles.
- Lower right section (proteins): Include high-quality proteins from sources such as chicken and seafood. Eat red meats like beef and pork in moderation, and avoid processed meats such as ham and bacon.
How to Avoid Gaining Weight When Eating Out?
Cai noted that it is indeed more difficult for people who often eat out to lose weight. This is because most restaurants often add large amounts of sugar, oil, and salt in their cooking and seasoning practices, which can lead to weight gain if eaten frequently.
- Prevent: Eat less before a meal. For example, if you know you will be having cake for afternoon tea, eat a lighter lunch and choose low-fat options. Alternatively, exercise beforehand. Cai shared that he does weight training before a meal to deplete muscle glycogen, allowing room in the muscles for sugar to be stored there instead of being stored as fat.
- Compensate: If you overeat at one meal, reduce your portions at subsequent meals or increase calorie burn through exercise.
- Relax: When enjoying a big meal or sharing dessert with friends, avoid feeling stressed or guilty. Maintaining a positive outlook, relaxing, and enjoying life will help you stay motivated and support long-term weight management.













