- Prevention of arteriosclerosis, cerebral infarction, and myocardial infarction
- Anti-aging effects
- Improved memory
- Prevention of osteoporosis
- Prevention of cancer
- Enhanced skin health
- Protection against colds and food poisoning
- Support for digestive health
- Weight loss
Why does natto offer these health benefits, and what precautions should be taken when eating it?
Exceptional Health Food
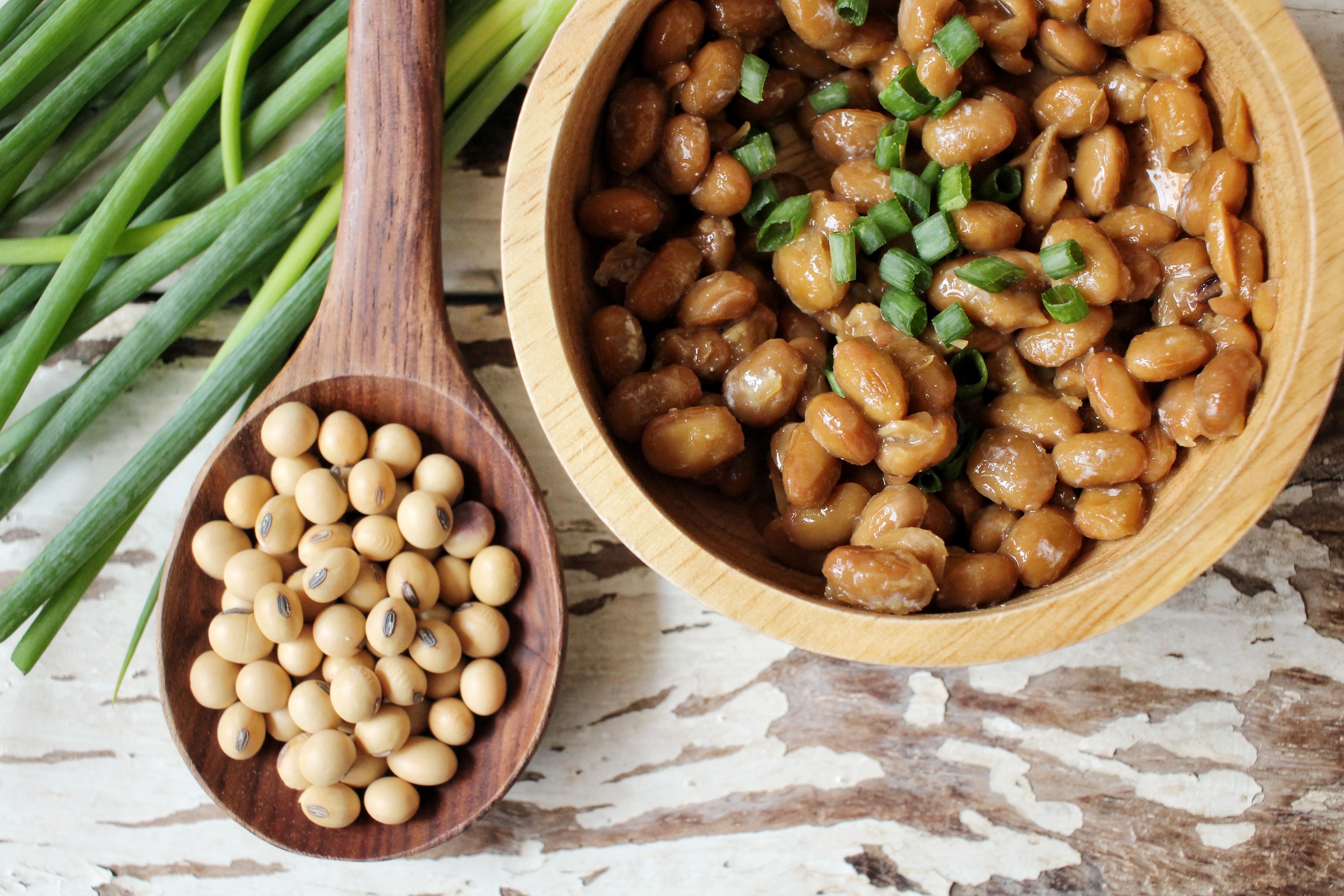
Natto’s health benefits are closely tied to its unique production process. It is made by steaming soybeans and then wrapping them in straw, which maintains a specific temperature that allows the natural Bacillus natto bacteria in the straw to ferment the beans. The Japanese have been eating natto for more than 1,000 years. Its production method is similar to that of Chinese fermented soybeans (douchi), which are also known for their health benefits.
6 Major Health Benefits
1. Promotes Digestion
Natto is beneficial for regulating digestive function and can help treat conditions such as dysentery, infections, gastrointestinal inflammation, bloating, indigestion, constipation, and incomplete bowel movements.
2. Prevents Osteoporosis
The vitamin K produced by microorganisms in natto, known as K2, differs from the K1 form found in vegetables. In the human body, vitamin K2 can also be biosynthesized by gut bacteria. In addition to promoting the formation of bone calcium, vitamin K2 helps prevent excessive calcium loss from bones, contributing to the prevention of osteoporosis.
3. Prevents Blood Clots
Nattokinase, produced during the fermentation of natto by Bacillus natto, is a natural substance with potent blood clot-dissolving properties found in the proteins of fermented natto. Animal studies have shown that nattokinase remains active as it passes through the acidic environment of the stomach and the alkaline conditions of the intestines.
4. Prevents Cancer
A study published in the Japanese Journal of Clinical Oncology suggested that regular consumption of natto may be associated with a lower risk of developing breast cancer in women.
5. Enhances Memory
Natto contains lecithin, which has been shown to enhance short-term memory. This is particularly beneficial for students and people with hectic work schedules.
6. Supports Weight Loss
A study published in the Journal of Functional Foods found that components in natto can promote fat metabolism, which may aid in weight loss.
Optimal Times for Consumption
Natto can be eaten every evening, but it is advisable not to eat it on an empty stomach, as its high fiber content may cause discomfort for those with digestive issues.
5 Groups of People Who Should Avoid Natto
For healthy individuals, moderate consumption of natto usually poses no side effects. However, people with the following conditions and situations should consult a doctor before eating natto:
- Impaired kidney function: Natto is made from soybeans, which are high in protein and can place an additional burden on the kidneys.
- Gastrointestinal diseases: People with stomach ulcers, dyspepsia, gastritis, or frequent stomach pain should limit their consumption of natto, as it contains a high amount of dietary fiber, which can place a significant burden on the stomach.
- Gout: Natto is a soybean product high in purines, which can exacerbate gout symptoms.
- Blood clotting disorders or taking anticoagulant medication: Natto is not recommended for people with bleeding wounds or those recovering from surgery. Additionally, it may interfere with the effectiveness of anticoagulant medications.
- On antihypertensive medication: Nattokinase can enhance the effects of blood pressure medications, potentially leading to excessively low blood pressure. Therefore, it is advisable to avoid eating natto concurrently with these medications. Individuals taking blood pressure medication should consult their primary care physicians before consumption.
Having learned about the Japanese secret to longevity—natto—consider incorporating it into your diet if you wish to combat aging and prevent blood clots.