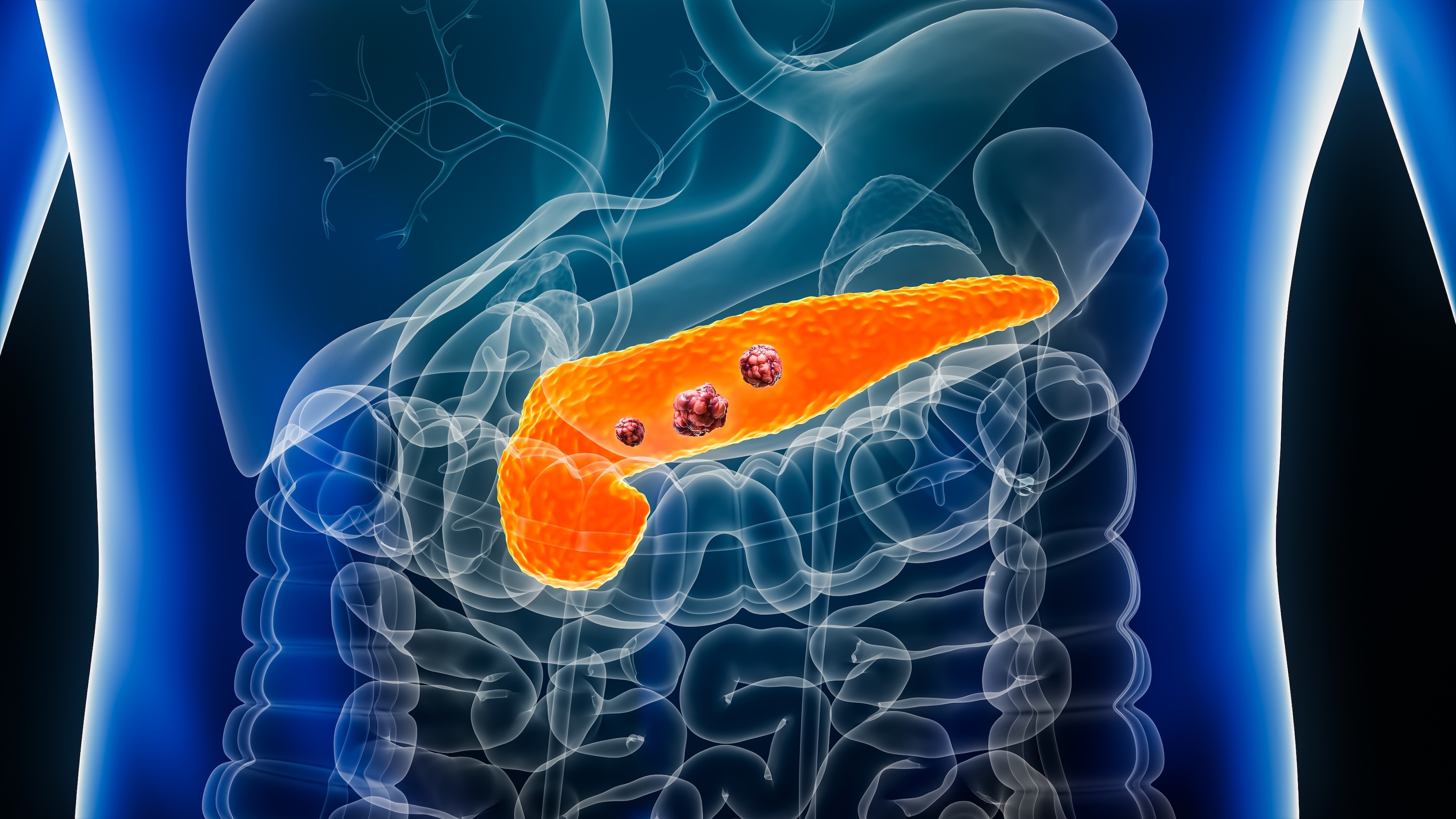
Pancreatic cancer is often called the “king of cancers” due to its difficulty in early detection and its high mortality rate. On the “Health 1+1” program, Guo Shifang, director of the Department of Integrative Medicine at Chi Mei Medical Center in Taiwan, explained that abdominal pain linked to pancreatic cancer has distinct characteristics and stressed the importance of seeking immediate medical evaluation if such symptoms arise.
About 66,440 new cases of pancreatic cancer are expected to be diagnosed in 2024, with 51,750 deaths projected during the same period, according to the National Cancer Institute. Pancreatic cancer accounts for 3.3 percent of all new cancer cases in the United States but is responsible for 8.5 percent of all cancer-related deaths.
Recognizing Abdominal Pain in Pancreatic Cancer
The pancreas is positioned behind the stomach, with the psoas major muscle situated directly behind it. When inflamed or affected by cancer, the pancreas can press on the lower back muscles, causing pain that radiates backward.
Guo described the typical characteristics of abdominal pain caused by pancreatic cancer:
- The pain occurs in the retroperitoneal area, similar to the stomach but deeper, often accompanied by an aching sensation in the back.
- Pressing on the affected area tends to intensify the pain.
- The discomfort worsens when the body is upright, leading to a tendency to bend forward. Lying on one’s side with knees bent and the body curled can help alleviate the pain.
- Pancreatic cancer most commonly develops in the head of the pancreas, located near the common bile duct. When this occurs, the pain may radiate to the chest and shoulders.
Other Common Symptoms
The pancreas serves both exocrine and endocrine functions. Its exocrine cells produce digestive enzymes, while its endocrine glands release hormones such as insulin to regulate blood sugar levels. Therefore, common symptoms of pancreatic cancer also include loss of appetite, rapid weight loss, jaundice, and diabetes.

Common symptoms of pancreatic cancer. (The Epoch Times)
A 2018 review indicated that over 85 percent of pancreatic cancer patients experience weight loss by the time of diagnosis. A patient weighing over 154 pounds (70 kilograms) could lose 44 to 66 pounds (20 to 30 kilograms) within just two to three months, Guo noted.
When a tumor in the head of the pancreas compresses the bile duct or when cancer cells invade it, bile secretion can become obstructed. This often leads to jaundice-related symptoms, including yellowing of the skin, yellowing of the whites of the eyes, dark tea-colored urine, and itchy skin.

Other symptoms of pancreatic cancer. (The Epoch Times)
The Link Between Diabetes and Pancreatic Cancer
New-onset diabetes is considered one of the warning signs of pancreatic cancer.
A study published in the Journal of the National Cancer Institute found that while long-term diabetes is a risk factor for pancreatic cancer, recent-onset diabetes may be a symptom of the disease. If there is no family history of diabetes, a sudden onset of the condition after age 50 could be linked to pancreatic inflammation or dysfunction, Guo said. This may occur because pancreatic tumors or chronic inflammation can impair the pancreas’s ability to regulate insulin production, either by damaging insulin-producing beta cells or by causing the release of inflammatory cytokines that disrupt glucose metabolism.
A systematic review highlighted that among patients with prediabetes or diabetes, every 0.56 mmol/L increase in fasting blood sugar raised the risk of developing pancreatic cancer by 14 percent.
Dietary Adjustment for Prevention
Regulating blood sugar is essential for preventing pancreatic cancer.
“We should avoid overworking the pancreas and allow it to rest,” Guo said. She added that consuming excessive amounts of carbohydrates and fats in a single meal forces the pancreas to produce large quantities of insulin and digestive enzymes to process them. This overexertion increases the risk of pancreatic inflammation.
Acute pancreatitis can cause the pancreas to be damaged by its own digestive enzymes, while chronic pancreatitis greatly increases the risk of pancreatic cancer.
Guo outlined the following dietary recommendations to help lower the risk of pancreatic cancer:
- Limit the intake of carbohydrates and fats. A diet high in refined carbohydrates and unhealthy fats can contribute to obesity and insulin resistance, both of which are linked to an increased risk of pancreatic cancer.
- Avoid high-temperature cooking methods, such as stir-frying and deep-frying. These methods can generate carcinogenic compounds, such as heterocyclic amines (HCAs) and polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons (PAHs), which may increase cancer risk.
- Avoid pickled and processed foods. While some pickled foods are healthy due to their probiotic content, the traditional pickling process using salt or nitrates can sometimes lead to the formation of nitrosamines, which are carcinogenic compounds. Additionally, some processed foods may also contain these harmful chemicals.
- Steer clear of high-sugar foods, including excessive consumption of fruits. While fruits are generally healthy, consuming large quantities of high-sugar fruits can lead to elevated blood sugar and insulin levels, which are associated with an increased risk of pancreatic cancer. Moderation and balancing fruit intake with other nutrient-dense, low-sugar foods are key.
“We do not need to live like monks. An occasional indulgent meal is likely fine, but frequent overeating can lead to various health issues,” Guo said.
Risk Factors for Pancreatic Cancer
Smoking is a significant risk factor for pancreatic cancer.
Studies show that smokers are more than twice as likely to develop pancreatic cancer compared to non-smokers.
Guo also emphasized minimizing exposure to secondhand smoke, cooking fumes, and incense smoke, even without being a smoker.
According to Cancer Research UK, 70 percent of chronic pancreatitis cases are attributed to long-term heavy alcohol consumption. Chronic pancreatitis is associated with an increased risk of pancreatic cancer.
Stress as a Trigger for Cancer Development
Managing stress and maintaining emotional balance are crucial for cancer prevention.
A recent case-control study found that pancreatic cancer patients were significantly more likely to have experienced major stressful events in the past five years, such as the loss of a loved one, divorce, or financial hardships.
A 2018 animal study suggested that the connection between stress and pancreatic cancer may be hormone-related. Stress can overstimulate the sympathetic nervous system, causing a surge in adrenaline release that promotes tumor growth.
According to Traditional Chinese Medicine (TCM), emotional stress can lead to energy stagnation and poor blood circulation in the body, a condition referred to as “qi stagnation and blood stasis,” Guo noted. This means that tumors are more likely to develop in areas where qi and blood become obstructed.
Pancreatic Cancer Screening Recommendations
Guo recommends that anyone with suspected symptoms of pancreatic cancer start with a blood test to check for markers such as
CA 19-9, a protein often produced by pancreatic tumor cells and released into the bloodstream. Elevated levels of CA 19-9 can indicate pancreatic cancer, though they are not specific to the disease and may also be elevated in other conditions, such as pancreatitis or bile duct obstruction.
If abnormalities are detected, further imaging tests, such as an ultrasound or CT scan, may be necessary to evaluate the pancreas more closely. However, these tests alone are not definitive for diagnosing pancreatic cancer. The only way to confirm the presence of cancer is through a biopsy, where a small sample of tissue is taken from the pancreas and examined under a microscope for cancerous cells.